August Luminosity and New Antiproton Source Stacking Record
Thursday, August 16
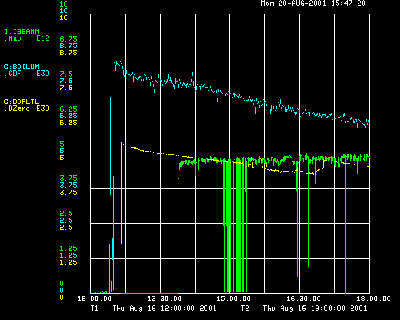
At 1 PM, TeV experts set a new luminosity record for this run of 7.9E30. This record is important because luminosity is a measure of particle interaction. (See graphic) The higher the luminosity, the greater the chance of creating quarks. Please visit the following links to discover how Fermilab's experiments use quarks: http://www-cdf.fnal.gov for CDF and http://www-d0.fnal.gov/public/index.html for D0. Fermilab's record for luminosity was set on May 10, 1995, with a level of 2.5E31.
Saturday, August 18
The Main Injector (MI) and the Antiproton Source (Pbar) set a new Fermilab record for stacking antiprotons. For more than an hour they stacked at 10.2 mA per hour. They averaged 10 mA per hour for about three hours. A milliamp is a current measurement that equals 1X1010 antiprotons, or approximately 10 billion particles. When Pbar experts resumed stacking after the MI installation back in December of 1999, stacking rates were 20 micro-amps per hour. New records like this are only attained through the contributions of many people, reliable operations, and various upgrades such as the Debuncher and Stack Tail cooling upgrades and the Accumulator lattice upgrade. Also, the new MI can delivery higher intensities than the Main Ring. This achievement is simply a step not an end; the next goal is 20 mA per hour.
|